🔹 1. Preparation
- Verify identity: Confirm the patient’s name, age, and medical record.
- Explain procedure: Reduce anxiety and get cooperation.
- Hand hygiene: Wash hands and wear gloves.
- Gather supplies: Tourniquet, alcohol swabs, sterile needle, collection tubes, gauze, tape/bandage, disposal container.
🔹 2. Patient Positioning
- Patient sits or lies comfortably.
- Arm extended and supported with palm facing upward.
🔹 3. Site Selection
- Common site: Median cubital vein (inside of elbow).
- Alternative: Cephalic vein, basilic vein, or dorsal hand veins.
- Avoid areas with infection, scars, or IV lines.
🔹 4. Site Preparation
- Apply tourniquet 3–4 inches above site to engorge veins.
- Palpate vein with index finger.
- Clean site with 70% alcohol in circular motion, allow to dry.
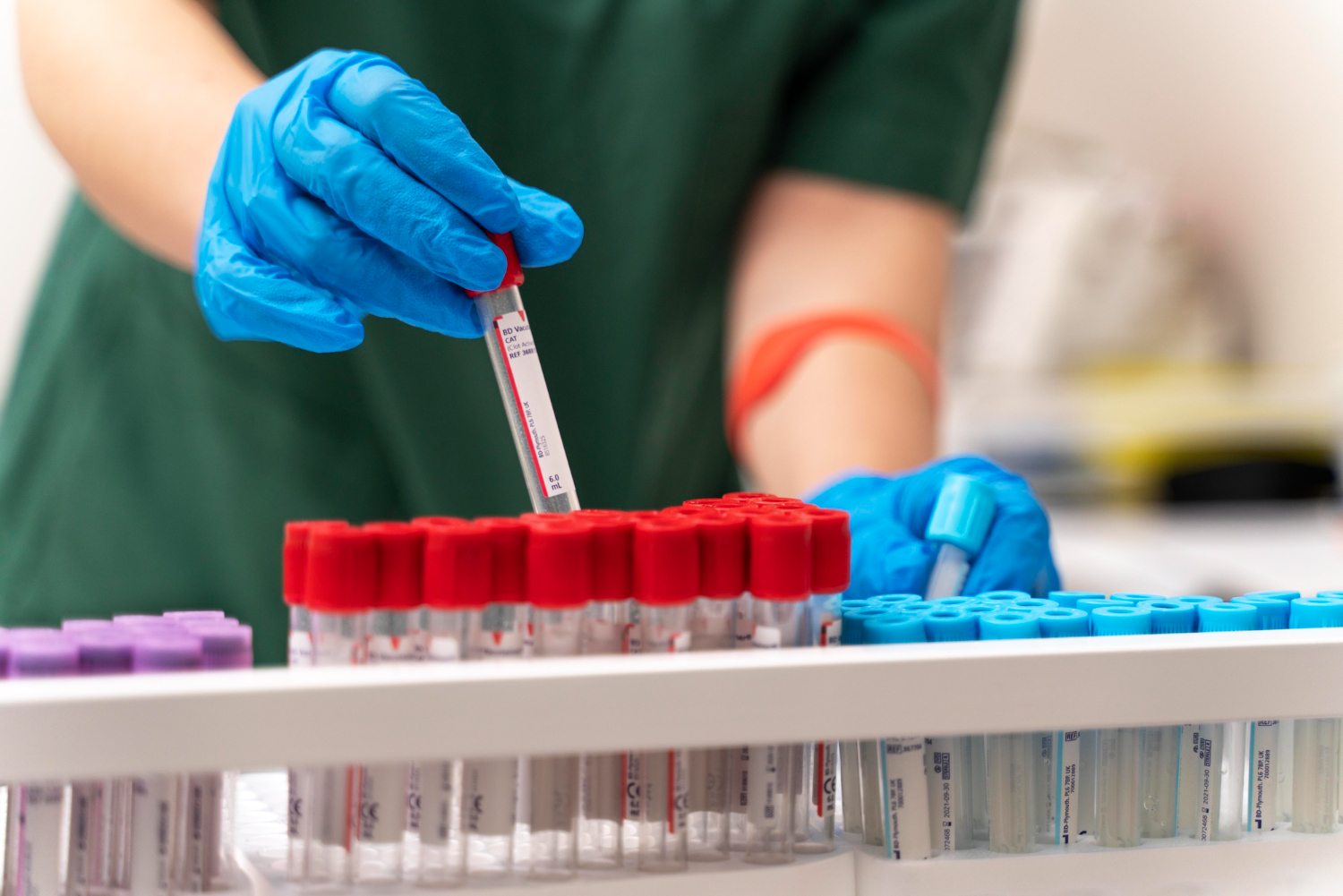
🔹 5. Venipuncture (Blood Collection)
- Insert sterile needle bevel up at a 15–30° angle.
- Blood flows into syringe or vacuum tube.
- Fill required tubes in correct order of draw (to prevent contamination).
🔹 6. Post-Collection
- Release tourniquet before withdrawing needle.
- Withdraw needle smoothly, immediately apply gauze with pressure.
- Ask patient to hold firm pressure for 2–5 minutes.
- Apply bandage.
🔹 7. Labeling & Documentation
- Label tubes at bedside (patient ID, date, time, collector’s initials).
- Complete lab forms and transport samples as per protocol.
🔹 8. Disposal & Safety
- Dispose of needle in sharps container immediately.
- Remove gloves, wash hands.
- Follow infection control protocols.
✅ Key Safety Tips
- Always follow universal precautions.
- Use the correct tube type (EDTA, citrate, heparin, serum).
- Avoid prolonged tourniquet use (can cause hemoconcentration).
- Never draw blood from a site below an active IV line unless documented.